What is Down syndrome?
Down syndrome is a disorder in the amount of chromosomes that makes up the human body. Down syndrome is sometimes referred to as Trisomy 21, the disorder leads to defects in the mental, and physical growth of a child. The features of Down syndrome may vary in each affected individual, and studies have shown that the condition cannot be prevented.
What causes of Down syndrome?
In most cases, curious persons may wonder what causes Down syndrome. Down syndrome is caused by the presence of an additional duplicate of genetic material on part, if not all, of the 21st chromosome, and this is abnormal. There should be a total of 46 chromosomes in each human cell, 23 of which you get from your mother, and the other 23 from your father. If a few, or all cells have an additional Y -chromosome (in males), complete ,or partial duplicate of chromosome 21, then this is evidence that Down syndrome is present.
The most prevalent type of Down syndrome is referred to as Trisomy 21. Trisomy 21 depicts cases where individuals possess 47 chromosomes, as opposed to 46. This is as a result of an abnormality in the division of cells, also referred to as non-disjunction. Non- disjunction will leave an egg cell with an additional copy of chromosome 21, either before, or during conception.
Ninety- five percent (95%) of what causes Down syndrome results from Trisomy 21, with approximately eighty-eight percent (88%) resulting from non-disjunction of the mother’s egg cell. The other five percent (5%) is as a result of two other types of Down syndrome conditions called Mosaicism and Robertsonian Translocation. Mosaic Down syndrome occurs when the body has normal cells, as well as Trisomy 21. Robertsonian translocation results when a part of chromosome 21 is detached during the cell division process, the detached part then attaches itself to another chromosome, in most cases it is chromosome 14. The additional part of chromosome 21 will cause a person with Down syndrome to appear physically normal, as well as put them at greater risk of giving birth to a child with an extra 21st chromosome.
The risk of having a child with Down syndrome, increases as the age of the prospective mother increases. The genetic material associated with Down syndrome can be linked to the mother as well as the father, but in most cases it is linked to the mother.
Characteristics of a person with Down syndrome
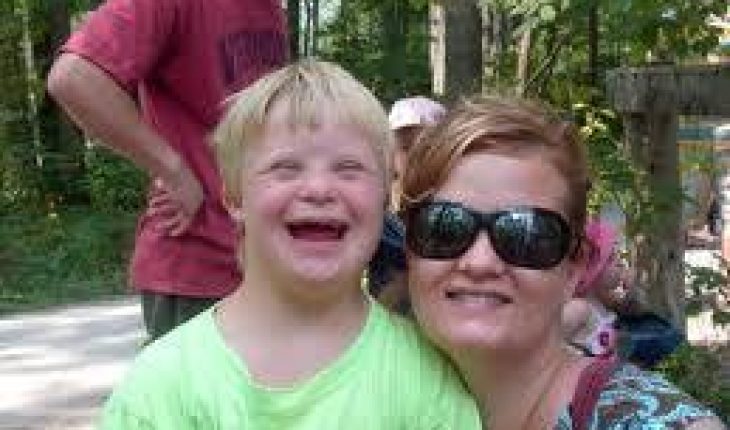
It is very easy to identify an individual with Down syndrome. Their eyes are usually slanted upwards, their nasal bridge is usually flat and their tongue is almost always protruding. Their cognitive development may vary, but is usually is classified as mild to moderate retardation. Down syndrome affected children usually experience speech delays, and sometimes need the assistance of a speech therapist. Their development physically is also slow, as they usually take a longer time to walk than a normal child, sometimes it may take them up to four years to take their first step. They are however, still able to live a relatively normal lifestyle.