Temporal arteritis is a grave disorder which results in inflammation of the medium and large arteries within the head. These arteries provide important oxygenated blood to parts of the head and the brain. The temporal arteries are usually affected by temporal arteritis. These arteries pass along the temple region near to the eye. If these arteries become swollen they will be unable to sufficiently supply oxygen, and nutrients to the head, and areas of the brain. Complications which may result from temporal arteritis include a stroke, or blindness. This possibility exists particularly if it was not diagnosed and treated speedily.
Cranial arteritis and giant cell arteritis are also used to refer to temporal arteritis. It is regarded as an autoimmune disorder. The immune system in an autoimmune disorder views the regular tissues and cells as possibly harmful entities and assaults them. This results in the inflammation. The reason for this is unknown in a lot of temporal arteritis cases. On the other hand, growing old possibly has a part in the occurrence and people over fifty predominantly have the disorder. Additionally it is most widely seen in women than in men.
Temporal arteritis is not essentially a common disorder. It is however the most typical reason for vasculitist. The disorder additionally causes a vast number of neurological symptoms which may impact on the eyes and vision, face, head and the body on a whole. It may be treated, however, if it goes without treatment, then it can lead to significant complications.
Symptoms of temporal arteritis
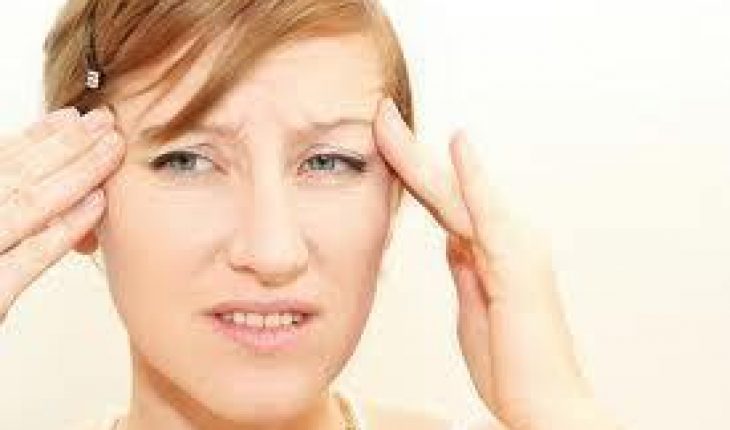
Symptoms of the disorder may vary among individuals. Its development in the main, affects the nervous system. It has the ability however, to affect different parts of the body. The general symptoms of temporal arteritis are headaches, shoulder pain, hip pain, fever, pain in jaw after, or while chewing, and blurred vision. There are other symptoms that may be experienced from the development of temporal arteritis such as weight loss, tongue pain, throat pain, or coughing.
How is temporal arteritist diagnosed
Diagnosing temporal arteritis involves doing a complete medical history. This will take into account the symptoms. A physical and an eye examination are also required. A complete blood test (CBC) and an ESR which is erythrocyte sedimentation rate should also be incorporated. These will detect inflammation taking place in the body.
In cases where temporal arteritist is suspected, a temporal artery biopsy will be the key diagnostic test carried out. The test requires that a tiny sample of the temporal artery is taken and this will be examined beneath a microscope for changes in inflammation which suggest temporal arteritis. In addition to these different tests could be carried out to assess overall health, and assist in finding out if there is damage to the brain, or complications arising from the disorder. Testing includes CT scan and MRI which are image tests that can identify any damage to the brain.