Hyperthyroidism is characterized by an over activity of the thyroid gland. This over stimulation will result in the over production of T? (triiodothyronine) and T? (thyroxine) which are both thyroid hormones produced by the thyroid gland in vertebrates. This over production of (T? and T? ) can cause a toxicity of thyroid hormones or thyrotoxicosis.
Classification of hyperthyroidism
T? and T? are endocrine hormones produced by, and secreted in the thyroid gland. However, for these hormones to be secreted, the thyroid gland has to be stimulated by thyroid stimulating hormone produced, and secreted in the pituitary gland in the brain. The pituitary gland in turn has to be stimulated by thyrotrophic releasing hormone, produced and secreted by the hypothalamus, also in the brain. The production of T? and T? is thus regulated by a negative feedback mechanism. There are three types of hyperthyroidism which can originate in any of the three organs previously named.
Primary hyperthyroidism
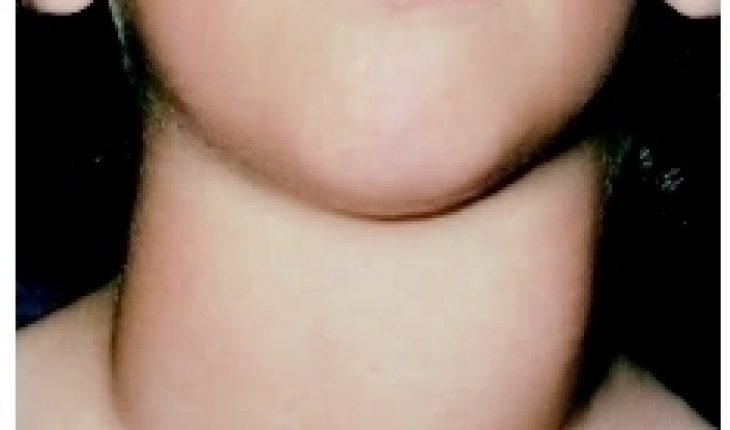
Primary hyperthyroidism occurs at the level of the thyroid gland, and is characterized by an over production in the thyroid hormones, T? and T?. This may be a physiological problem occurring with the gland where it is enlarged, and produces excessive amounts of these hormones.
Secondary hyperthyroidism
Secondary hyperthyroidism occurs at the level of the pituitary gland, and is characterized by an over production in thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH).
Tertiary hyperthyroidism
Tertiary hyperthyroidism occurs at the level of the hypothalamus, and is characterized by an over production in thyrotrophic releasing hormone (TRH). Sometimes secondary, and tertiary hypothyroidism are not differentiated because it is unnecessary. If the problem is not found to be at the primary level, then it is at the secondary or tertiary level. Since the treatment is for a thyroid hormone no matter the level, it is considered an unnecessary expense to explore further.
Causes of hyperthyroidism
Graves’ disease is a common cause of hyperthyroidism. It is characterized as a disease where the thyroid gland is over active, thus stimulating the excessive or over production of T? and T?.
Toxic thyroid adenoma is a benign tumor on the thyroid gland. This tumor is an over proliferation of cells of the thyroid gland. The increased number of cells increases the production of thyroid hormone and thus causes a toxicity of thyroid hormones in the body.
Toxic multi-nodular goiter causes the over production of thyroid hormones because of functional autonomous nodules formed on the thyroid gland.
Thyroiditis is an inflammation of the thyroid gland. This inflammation causes an initial over production of thyroid hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
- Weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Hyperactivity
- Muscle pain
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Increased bowel movements
- Long term hyperthyroidism, or hyperthyroidism left untreated for long period can cause a loss of calcium from the bones and osteoporosis.
- Various cardiovascular effects such as; palpitations and arrhythmias.
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Absence of the menstrual period
- Hypoglycemia or low blood sugar.
- Tremors
- Apathy