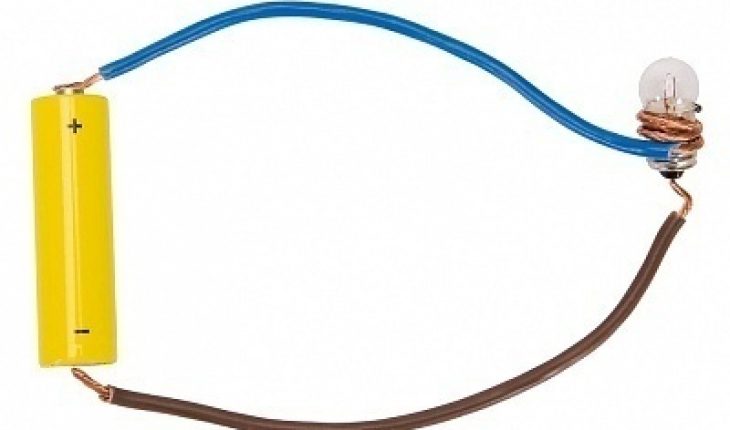
If you are wondering how does a battery work, remember that they change chemical energy to electrical energy. Batteries have chemicals that produce reactions that are electrochemical in nature. By generating electrical power, they become portable generators.
Inside a Battery
Batteries have cells that are capable of transmitting voltage. A couple of half-cells are linked with an electrolyte. This is responsible for the charge transfer. The majority of commercially available batteries are comprised of zinc/carbon or alkaline/manganese.
A half-cell or single battery has a positive electrode while the other is negative. Electrons gather on the negative terminal. They flow between the negative and positive terminals assuming a wire / conductor is present. That is why one battery is positioned with the negative electrode and the other directed at the electrolyte (conductor).
The electrolyte is linked to positive and negative charges. Together they comprise the circuit of a battery. Keep that in mind when studying how does a battery work.
This is a basic description of battery contents; some may have different configurations or setups.
Separator and Conductor
If positive and negative cells are not joined to a conductor, there will be no energy draining. There will be no chemical reaction either. In some cases, half cells are contained in the same area. In this type, a porous electrolyte functions as a conductor and separator. The separator prevents the electrodes from making contact. It also provides the charge required to produce electrical power.
Energy in Batteries
Energy contained varies because they have varying electric potential ratings and contained charges. However, they all function via chemical reactions. The energy in these batteries is finite. Even rechargeable batteries will eventually expire. The lifespan will depend on the energy contained. It also hinges on how much energy the device using the battery is consuming.
Charges
If you are still inquiring how does a battery work, remember their milli-ampere hours (mAh) ratings. It determines what charge is in the unit. The rating / value depend on the contained energy. The ampere determines coulomb (charge) per second. A rating of 2,650 mAh means it has a (2,650 mAh) (3600 s)/(1 hour). Batteries are also classified by electric potential (voltage, V).
Sometimes the rating is by joule, J which is transmitted by per coulomb (J/C). A standard AA battery usually has a rating of 1.2v. If you are looking for the energy in a battery, just add the potential rating and entire charge.