What is Granuloma Annulare?
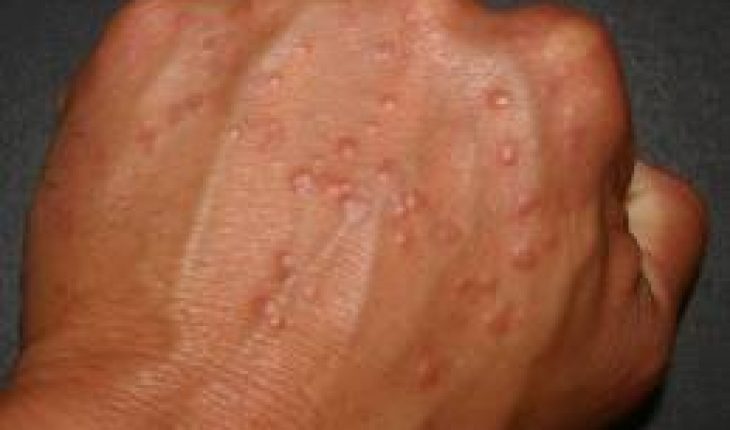
Granuloma annulare is a skin condition that occurs generally in childhood, the teenage years, adolescence and to a lesser extent in adults. The skin disorder can appear anywhere on the body, and may sometimes affect large sections of the body. It is not typically associated with any other symptoms with the exception of occasional itching, or tenderness when the area is irritated. Granuloma annulare may disappear within a few weeks, or months without treatment and will not cause scarring. However, the condition may return at the same location, or a different area of the body in future.
Types of Granuloma Annulare
The manifestation of the disorder is categorized as follows:
Localised granuloma annulare
Bumps that are the same colour as the skin may form over the joints, and knuckles in a ring like pattern. The ring will normally have a depressed centre. It is typically found on the back of either, or both hands, and fingers.
Generalised granuloma annulare
These may appear pinkish in colour and can be seen on large areas of the body in the form of papules that create a ring like shape. The diameter is usually 10 cm, and is likely to be found near the armpits or groin. In a few cases the presence of this type of granuloma annulare may indicate another underlying condition like diabetes mellitus, lymphoma, or HIV.
Deep granuloma annulare/ Pseudo-rheumatoid nodules
The areas affected will normally be the edges of the scalp, the finger tips, and the shins. The nodules will feel rubbery when touched, and they will be embedded below the dermis. They are similar in appearance to rheumatoid nodules, however they occur in people who do not suffer from the associated condition rheumatoid arthritis.
How is the disorder diagnosed?
The condition may be diagnosed based on the presentation of the rash or nodules. A dermatologist can usually identify granuloma annulare upon sight, after a physical examination. However, there are cases where the condition may not be completely obvious. In such instances, a biopsy is performed to rule out any other condition as the primary cause. A positive biopsy for the disorder will show necrobiotic degeneration of the collagen found in the dermis with evidence of an ongoing inflammation.
What treatment is available for granuloma annulare?
Often treatment is not essential as the condition will clear up on its own. However, in cases where the patient is uncomfortable with the rash, or where it continues for more than a few months then a course of treatment may be recommended. The disorder does not produce scarring, therefore, rashes that clear up on their own will not leave marks.
Typical treatment methods include using steroids that can be injected in the bumps to reduce their size. In addition cryotherapy may be performed to remove small plaques. The use of topical treatments may also reduce the size of nodules. Where the condition is found in several areas of the body other treatments may be used as recommended by your health care provider.