What exactly is an Active Directory?
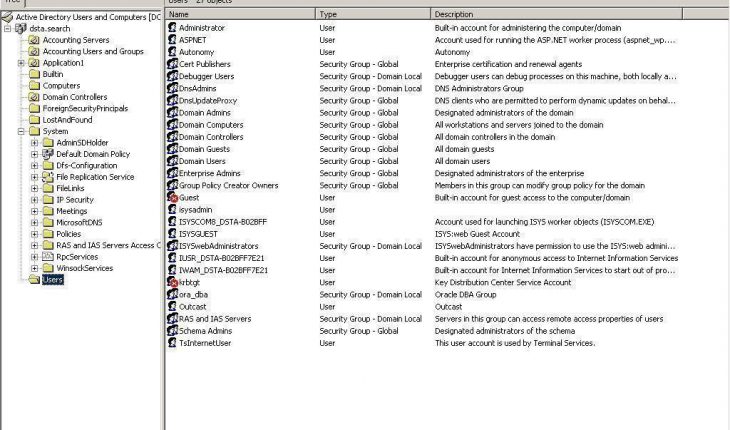
An active directory is a directory structure used on computers and servers that work on the base of Microsoft Windows. The main purpose of the active directory is to store information and data about domains and networks. Originally created in 1996 this was predominantly used for online information and was first used with Windows 2000. Active directory also known as AD does a whole lot of functions. This includes the ability of providing information on objects and also organizing these objects for easy retrieval and access. The AD also allows access by end users and administrators. Administrators are allowed to set up security for the directory.
Active directory is in form of a hierarchal structure. The structure is made up of three main categories. The resources include hardware such as printers and services for the end users like the web mail servers and objects which are the most important function of the domain and the network.
The interesting thing to make a note of is the framework for the objects. It is important to remember that the object can be hardware and such as a printer, end user or security settings set by the administrator. These objects also have the ability to hold other objects within their file structure. All objects have an ID which is usually an object name also known as folder name. In addition to holding objects within objects, these objects also have their own attributes which allows it to be characterized by the information. These are called setting or characterization schemas by the IT professionals.
The type of schema created for a folder will decide how the objects are used. For example some schemas cannot be deleted but only deactivated. Some other type of schemas with other attributes can be deleted all together. For instance, a user object can be deleted but administrator object cannot be deleted.
Understanding active directories is easier when the framework of the objects is known. An active directory can be viewed in three levels; these levels are called as forests, trees and domains. The highest structure is called the forest; this structure is named so as one can see all the objects included in the forest within the active directory. Included within these forests are trees which hold one or more domains. Further down the structure of an active directory the domains are single. For example in a large organization there are lots of users and processes. In this setup the forests are a network of end users and specific computers at a given set location. These forest directories contain within them trees that hold information on specific objects like system, program data, domain controllers etc. Furthermore there are objects within objects which can be controlled and categorized.
Use of active directories
In case you are a computer administrator in a large organization, you can easily update all the end users with new soft wares, patches, files etc by updating an object in a tree or a forest. Each object is made with a certain schema and certain attributes which are specific, the computer administrator reserves the rights to grant or deny access to the users on a particular set tree. Microsoft servers use the trust to determine if access should be granted or denied. The trust system is of two types namely transitive trusts and one way no transitive trusts. A transitive trust means when the trust goes further than two domains in a set tree, enabling two entities to access each others domains and trees.
The one way no transitive trust is when a user is granted access to another tree and domain but this also means that the other domain has no access to the other domains. To make it short and simple, it means that the network administrator has access to most trees in the forest including the end users domain, while the end user can access only his domain.
Active directories are a good and an efficient way of organizing a large organization’s computer network and data. In the absence of active directories it would be a tedious task to update each computer individually. Moreover, accessing a large network seems an impossible task.. Access to a large network is necessary to process data and report. Active directories need a lot of technical expertise but nevertheless make the work easier to handle and manage. They are vital for storing data and information on networks. If you think that you need to know more information you will be able to do that with the help of the internet in today’s world.